Mon - Saturday, 09:00 AM - 07:00 PM
Mon - Saturday, 09:00 AM - 07:00 PM
Abnormal uterine bleeding is a broad term that describes irregularities in the menstrual cycle involving frequency, regularity, duration, and volume of flow outside of pregnancy. Up to one-third of women will experience abnormal uterine bleeding in their life, with irregularities most commonly occurring at menarche and perimenopause. A normal menstrual cycle has a frequency of 24 to 38 days, lasts 7 to 9 days, with 5 to 80 milliliters of blood loss. Variations in any of these 4 parameters constitute abnormal uterine bleeding.
Abnormal uterine bleeding can also be divided into acute versus chronic. Acute AUB is excessive bleeding that requires immediate intervention to prevent further blood loss. Acute AUB can occur on its own or superimposed on chronic AUB, which refers to irregularities in menstrual bleeding for most of the previous 6 months.
PALM-COEIN is a useful acronym provided by the International Federation of Obstetrics and Gynecology (FIGO) to classify the underlying etiologies of abnormal uterine bleeding. The first portion, PALM, describes structural issues. The second portion, COEI, describes non-structural issues. The N stands for "not otherwise classified."
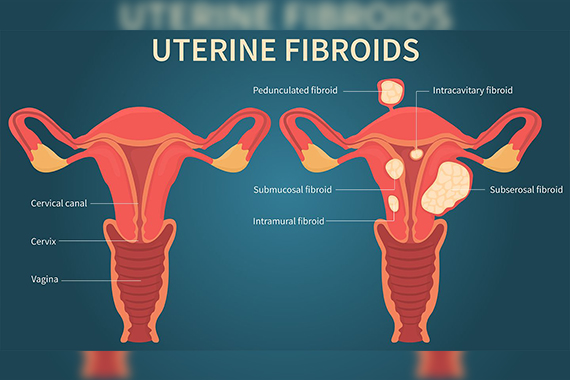
Fibroids are abnormal growths that develop in or on a woman's uterus. Sometimes these tumors become quite large and cause severe abdominal pain and heavy periods. In other cases, they cause no signs or symptoms at all. The growths are typically benign, or noncancerous